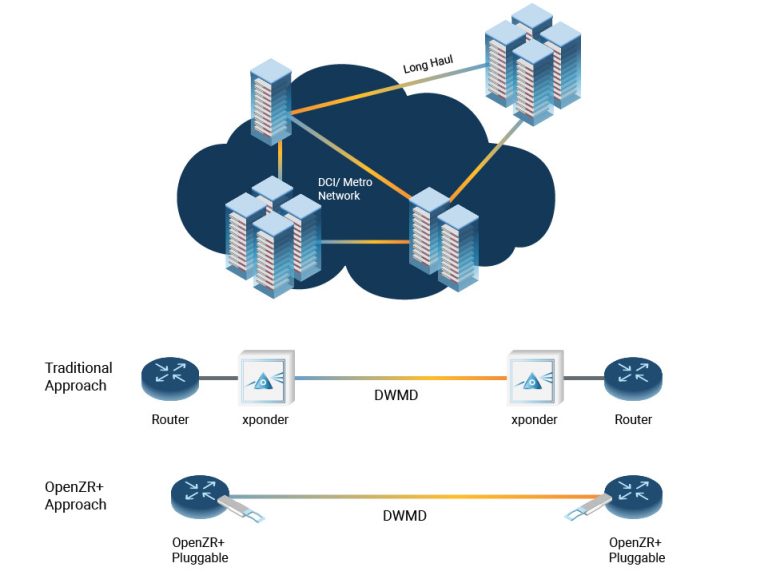
You have a challenge:
you need to connect one data center to another several kilometers away.
The work order specifies 810G fiber connections.
While you could run all eight pairs of fiber across the campus, this would be extremely expensive.
A more cost-effective solution is Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM).
Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) is a technology that allows you to combine multiple optical signals
with different wavelengths onto a common strand of fiber.
At one end of the link, the unit’s multiplexer (MUX) combines these signals to be transmitted over the common fiber.
At the opposite end, the unit’s demultiplexer (DEMUX) separates the signals.
Instead of running eight different pairs of fiber, you can install a MUX and DEMUX at each location to combine those
eight signals and transmit them over a single common pair of fibers.
There are many ways to address fiber scarcity issues, we are happy to guide you through all available options to help you find the perfect solution for your network.
How WDM Can HelpAs shown here, passive WDM can help add bandwidth to networks without increasing additional fiber.
For example, if there is a 10G link between two key locations on campus, a simple set of filters can increase the effective bandwidth of this link to 40G, 80G, or even 400G.
WDM offers benefits:
Customization:
Regardless of how many channels are needed, there is a filter set that is exactly right for your needs.
Reliability: Small campuses have limited capacity IT departments (sometimes just one person), which means time is of the essence. Passives require little to no maintenance once they are deployed. Their simple design means there is no need to worry about compatibility with your existing network equipment. Their durable construction also makes them built to last.
Affordability: Compared to upgrading your entire network, introducing active WDM (or adding additional fiber) or passive WDM products is a more budget-friendly solution.
Set up a free consultation with a GOIP Group expert engineer today by calling or visiting https://goipgroup.com.
The work order specifies 810G fiber connections.
While you could run all eight pairs of fiber across the campus, this would be extremely expensive.
A more cost-effective solution is Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM).
Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) is a technology that allows you to combine multiple optical signals
with different wavelengths onto a common strand of fiber.
At one end of the link, the unit’s multiplexer (MUX) combines these signals to be transmitted over the common fiber.
At the opposite end, the unit’s demultiplexer (DEMUX) separates the signals.
Instead of running eight different pairs of fiber, you can install a MUX and DEMUX at each location to combine those
eight signals and transmit them over a single common pair of fibers.
There are many ways to address fiber scarcity issues, we are happy to guide you through all available options to help you find the perfect solution for your network.
How WDM Can HelpAs shown here, passive WDM can help add bandwidth to networks without increasing additional fiber.
For example, if there is a 10G link between two key locations on campus, a simple set of filters can increase the effective bandwidth of this link to 40G, 80G, or even 400G.
WDM offers benefits:
Customization:
Regardless of how many channels are needed, there is a filter set that is exactly right for your needs.
Reliability: Small campuses have limited capacity IT departments (sometimes just one person), which means time is of the essence. Passives require little to no maintenance once they are deployed. Their simple design means there is no need to worry about compatibility with your existing network equipment. Their durable construction also makes them built to last.
Affordability: Compared to upgrading your entire network, introducing active WDM (or adding additional fiber) or passive WDM products is a more budget-friendly solution.
Set up a free consultation with a GOIP Group expert engineer today by calling or visiting https://goipgroup.com.