Software-defined WAN (SD-WAN) is a virtual wide area network (WAN) that relies on software technologies – like internet-based communication tunnels, software-driven network encryption, firewall software, etc. – to operate a mid-sized to large-scale computer network spread across locations. This article explains how SD-WAN works, its benefits, and the best SD-WAN solutions in the market.
What Is SD-WAN (Software-Defined WAN)?
Software-defined WAN or SD-WAN is defined as a virtual wide area network (WAN) that relies on software technologies – like internet-based communication tunnels, software-driven network encryption, firewall software, etc. – to operate a mid-sized to large-scale computer network spread across locations.
A software-defined wide area network (SD-WAN) uses software-defined technology and infrastructure. SD-WAN dissociates the networking hardware from the control mechanism and thus streamlines the WAN’s operation and management. Organizations that use SD-WAN solutions can build higher-performance WANs using inexpensive internet and at significantly lower costs than private WAN connection technologies such as multiprotocol label switching (MPLS).
SD-WAN solutions make it easier for organizations to manage firewalls and routers, upgrade software and firmware, virtual private networks (VPN), and remote clients through a centralized management interface. The centralized management control is used to securely and efficiently route traffic across the WAN directly to trusted providers such as software-as-a-service (SaaS) and infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS). It also minimizes labor costs by cutting maintenance costs and lowers the cost of equipment.
A software-defined wide area network (SD-WAN) uses software-defined technology and infrastructure. SD-WAN dissociates the networking hardware from the control mechanism and thus streamlines the WAN’s operation and management. Organizations that use SD-WAN solutions can build higher-performance WANs using inexpensive internet and at significantly lower costs than private WAN connection technologies such as multiprotocol label switching (MPLS).
SD-WAN solutions make it easier for organizations to manage firewalls and routers, upgrade software and firmware, virtual private networks (VPN), and remote clients through a centralized management interface. The centralized management control is used to securely and efficiently route traffic across the WAN directly to trusted providers such as software-as-a-service (SaaS) and infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS). It also minimizes labor costs by cutting maintenance costs and lowers the cost of equipment.
Benefits of SD-WAN
These figures express an increasing appetite for SD-WAN solutions from enterprises due to a slew of business benefits. These include:
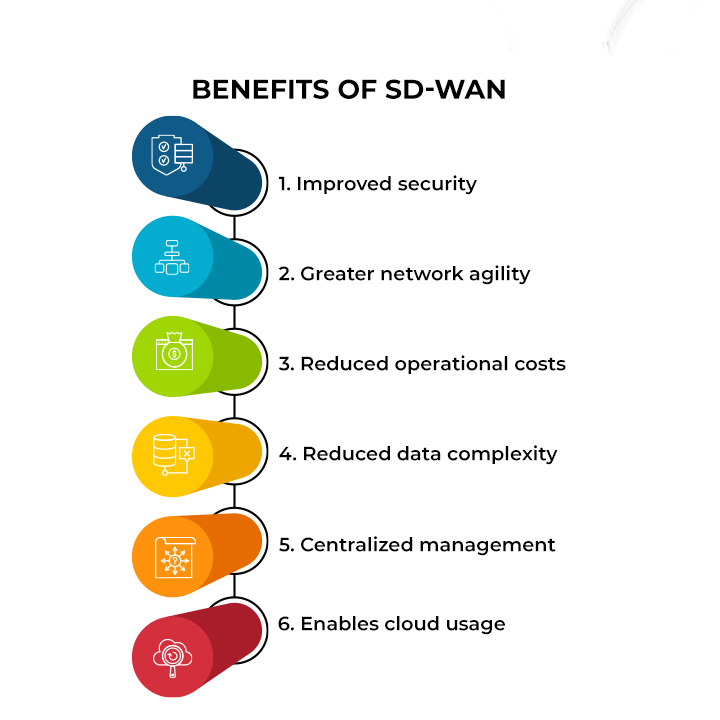
1. Improved security
In the recent past, business enterprises and other organizations have embraced advanced technologies to gain an edge against their competitors in the market. However, its adoption has brought on its fair share of problems in the form of cybercrimes.
Most SD-WAN solutions offer basic built-in security features like firewall and VPN functions that improve security for their users. Additionally, users looking for advanced security features can look for SD-WAN solutions offering features to prevent data loss, downtime, and legal liabilities. Popular SD_WAN solutions include next-generation firewalls (NGFW), intrusion prevention systems (IPS), encryption, and sandboxing capabilities.
Most SD-WAN solutions offer basic built-in security features like firewall and VPN functions that improve security for their users. Additionally, users looking for advanced security features can look for SD-WAN solutions offering features to prevent data loss, downtime, and legal liabilities. Popular SD_WAN solutions include next-generation firewalls (NGFW), intrusion prevention systems (IPS), encryption, and sandboxing capabilities.
2. Greater network agility
Users can configure SD-WAN to steer their business traffic through the most efficient route by prioritizing real-time services such as voice over internet protocol (VoIP) and business-critical traffic. SD-WAN, through its flexibility, allows users to vary bandwidth access via any local internet provider to promote increment in speeds to match real-time demand. Varying bandwidth using deduplication and compression also helps in reducing the total cost of ownership (TCO).
SD-WAN allows for bandwidth capacity to be scaled up or down through the direct addition of internet broadband connectivity. A single logical link can be formed when multiple WAN service types, such as direct internet or private multiprotocol label switching (MPLS), are bonded together.
Other optimization techniques that SD-WAN employs to improve network agility include data de-deduplication, data compression, and secure sockets layer (SSL).
SD-WAN allows for bandwidth capacity to be scaled up or down through the direct addition of internet broadband connectivity. A single logical link can be formed when multiple WAN service types, such as direct internet or private multiprotocol label switching (MPLS), are bonded together.
Other optimization techniques that SD-WAN employs to improve network agility include data de-deduplication, data compression, and secure sockets layer (SSL).
3. Reduced operational costs
According to a 2018 forecast survey by IDC Research, up to two-thirds of respondents expect to save 5-19%, while a quarter expect upwards of 39% savings when using SD-WAN technologies. SD-WAN technology allows for self-managed procedures and automation, which enables organizations to reduce the number of external IT experts required to carry out periodic tests and maintenance, thereby proving to be cost-effective.
SD-WAN aggregates multiple direct-to-internet (DIA) lines for WAN connectivity, thus reducing the overall cost for bandwidth as it requires less network hardware. Organizations can also easily set up new branches online at any location at less time and cost.
SD-WAN aggregates multiple direct-to-internet (DIA) lines for WAN connectivity, thus reducing the overall cost for bandwidth as it requires less network hardware. Organizations can also easily set up new branches online at any location at less time and cost.
4. Reduced data complexity
As small businesses use more technology solutions such as local, edge, and cloud-based applications, network complexity becomes a common problem. This is due to competition for limited bandwidth, which leads to poor network performance. It might also necessitate hiring more IT specialists on-site to manage local IT infrastructure, leading to increased costs. SD-WAN provides a solution through monitoring and alerting the performance of different data types to ensure enough bandwidth is allocated. Users can configure SD-WAN to prioritize critical traffic through the most efficient path to its destination to improve performance.
5. Centralized management
SD-WAN is usually managed through a centralized management interface that monitors it and manages traffic. From a single management portal, paths to applications are allocated according to criticality, new sites are provisioned, software and firmware upgrades are performed, and users can flex bandwidth from this point. Using a centralized management plan helps to reduce complexity and makes it easier to track applications and their performances from a single zone.
6. Enables cloud usage
Organizations are gradually adopting cloud-based services. SD-WAN enables users to access the cloud remotely without burdening the core network with additional traffic to manage and secure. This may promote cost savings for organizations looking to cut down on office space, equipment and rent as employees can work remotely. The need for additional IT experts to manage and secure data traffic is also minimized.
SD-WAN solutions improve cloud applications’ performance by emphasizing business-critical applications and allowing them to communicate directly to the internet. SD-WAN guarantees quality and optimizes data, followed by directing network traffic along the most efficient routes.
SD-WAN solutions improve cloud applications’ performance by emphasizing business-critical applications and allowing them to communicate directly to the internet. SD-WAN guarantees quality and optimizes data, followed by directing network traffic along the most efficient routes.
Limitations of WAN and how SD-WAN addresses them
During the early years, WANs required backhauling of all traffic from branch offices to a data center where they applied advanced security services. Traffic between the source and data centers was based on complex routing protocols such as transmission control protocol (TCP/IP) addresses and control list tables.
Ultimately, it leads to delays resulting in poor application performance, user experience, and huge costs due to expensive bandwidths. Users also had to incur expenses to install MPLS routers at each location. Performing upgrades on firmware or software took longer times due to network complexities. The network architecture was also not optimized for cloud infrastructure. The limitations of traditional WANs drove the change to a better SD-WAN technology that replaced MPLS.
SD-WAN is deployed in an organized way in branch offices and data centers. It is optimized for cloud infrastructure and associates cloud technology with mobile computing. It separates the data plane and control plane of the network. It has a centralized management interface where traffic is managed and monitored. It has a single management portal which reduces complexities and makes it easier to track applications, thus improving performance and operational efficiencies.
By providing lower-cost infrastructure and transport costs, an organization can save. SD-WAN provides end-to-end encryption over the entire network, providing secure connections to its users. Additionally, SD-WAN can prioritize traffic on business-critical applications and route it through the most efficient pathway.
Ultimately, it leads to delays resulting in poor application performance, user experience, and huge costs due to expensive bandwidths. Users also had to incur expenses to install MPLS routers at each location. Performing upgrades on firmware or software took longer times due to network complexities. The network architecture was also not optimized for cloud infrastructure. The limitations of traditional WANs drove the change to a better SD-WAN technology that replaced MPLS.
SD-WAN is deployed in an organized way in branch offices and data centers. It is optimized for cloud infrastructure and associates cloud technology with mobile computing. It separates the data plane and control plane of the network. It has a centralized management interface where traffic is managed and monitored. It has a single management portal which reduces complexities and makes it easier to track applications, thus improving performance and operational efficiencies.
By providing lower-cost infrastructure and transport costs, an organization can save. SD-WAN provides end-to-end encryption over the entire network, providing secure connections to its users. Additionally, SD-WAN can prioritize traffic on business-critical applications and route it through the most efficient pathway.
How Does SD-WAN Work?
The main objective of SD-WAN is to connect end-users and the applications, notwithstanding the location of these end-users. SD-WAN drives traffic as per the business requirements of the application. These business requirements vary from the priority of the application to must-enforced security policies or application performance required. Usually, critical mission applications are given the highest priority. The networking approach may vary from MPLS to broadband to 4G LTE.
The SD-WAN architecture separates the control and management functions, applications, and WAN transport services. It has a centralized control plane that stores and manages all the data on the traffic and applications. The centralized control plane monitors and adapts traffic to suit the application demand and delivers the optimum experience.
The following are features of SD-WAN that users should consider before choosing an SD-WAN solution model:
Encrypted overlay network: Traffic over the entire network must be encrypted to avoid any cyber threats leading to data loss. It should also be policy-driven.
Real-time monitoring: The chosen SD-WAN should be able to collect real-time data statistics.
Endpoints: The chosen SD-WAN must connect with every endpoint from any application and software.
Load balancing: This technique ensures that the bandwidth is efficiently utilized to manage several incoming and outgoing traffic requests.
Resiliency: The chosen SD-WAN should support redundancy and failover features.
Policy-based routing:
Algorithms that use real-time statistics to find the most optimal paths for a specific application should be included.
Data services independence: The SD-WAN should have the ability to connect to multiple stations with different categories of internet data services and hybrid deployments.
Advanced security and VPN features: The chosen SD-WAN should ideally have advanced security features such as a next-generation firewall, a security web gateway, and advanced cyber threat protection.
Mobility features: The SD-WAN should have mobility features such as access control, an advanced security parameter, and automatic ideal route selection that enable interactive interactions.
The SD-WAN architecture separates the control and management functions, applications, and WAN transport services. It has a centralized control plane that stores and manages all the data on the traffic and applications. The centralized control plane monitors and adapts traffic to suit the application demand and delivers the optimum experience.
The following are features of SD-WAN that users should consider before choosing an SD-WAN solution model:
Encrypted overlay network: Traffic over the entire network must be encrypted to avoid any cyber threats leading to data loss. It should also be policy-driven.
Real-time monitoring: The chosen SD-WAN should be able to collect real-time data statistics.
Endpoints: The chosen SD-WAN must connect with every endpoint from any application and software.
Load balancing: This technique ensures that the bandwidth is efficiently utilized to manage several incoming and outgoing traffic requests.
Resiliency: The chosen SD-WAN should support redundancy and failover features.
Policy-based routing:
Algorithms that use real-time statistics to find the most optimal paths for a specific application should be included.
Data services independence: The SD-WAN should have the ability to connect to multiple stations with different categories of internet data services and hybrid deployments.
Advanced security and VPN features: The chosen SD-WAN should ideally have advanced security features such as a next-generation firewall, a security web gateway, and advanced cyber threat protection.
Mobility features: The SD-WAN should have mobility features such as access control, an advanced security parameter, and automatic ideal route selection that enable interactive interactions.